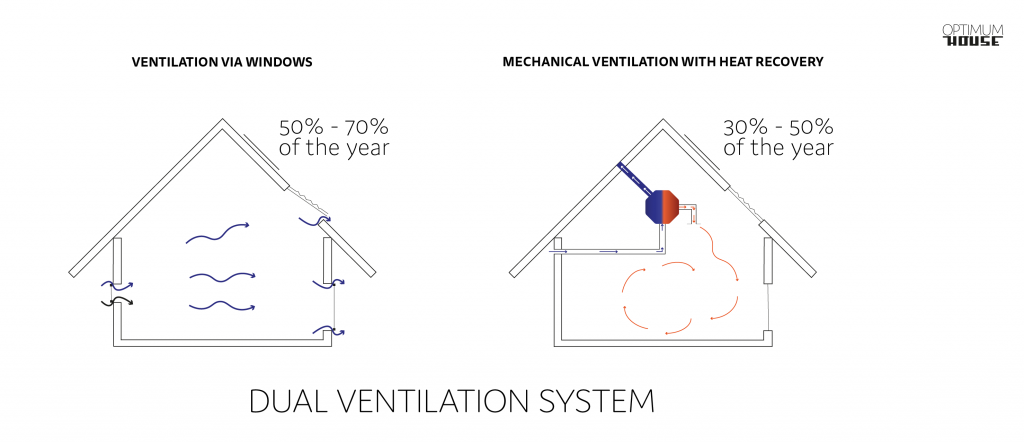
The high air-tightness of the Optimum House, due to the need to keep heat inside the building, requires careful planning of adequate and regular air exchange. In order to optimise the ventilation of the Optimum House to cater to temperate to cold zones of the Earth, a dual ventilation system has been planned, consisting of mechanical ventilation with heat recovery and automatic or semi-automatic ventilation via the windows.
Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery allows us to achieve significantly reduced heat loss during the heating periods due to air exchange during ventilation of the building. However, considering the fact that the numerous advantages are also accompanied by onerousness aspects of this solution (reducing the psychological and physiological well-being of the occupants due to getting cut off from the outside world, the cost of electricity consumed by the recuperation device, significant humidity reduction and the need to replace filters), mechanical ventilation should only be applied when natural ventilation involves excessive thermal energy loss. Natural ventilation via windows can be done automatically by means of controlling the windows selected for ventilation centrally (appropriate, available on the market fittings and simple controllable actuators move the window sash away from the frame all over its surface) or in a semiautomatic way whereby the opening of each window is programmed separately. In both cases, the selection of specific facade and roof windows for ventilation is, in view of their location and surface, aligned with the local building’s energy concept.
Back to Five energy tasks